Introduction: Wellhealthorganic Vitamin B12
In the realm of vitamins, Vitamin B12 stands out due to its critical role in maintaining various aspects of health. Found in a range of foods and available as a supplement, Vitamin B12 is essential for nerve function, red blood cell production, and overall metabolic processes. This in-depth guide from Wellhealthorganic.com delves into the benefits of Vitamin B12, its sources, symptoms of deficiency, and how it supports your health.
1. Understanding Vitamin B12
1.1. What is Vitamin B12?
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin that plays a crucial role in the production of red blood cells, DNA synthesis, and proper nerve function. It is one of the eight B vitamins, each contributing to energy metabolism and overall well-being.
1.2. How Vitamin B12 Works
Vitamin B12 is absorbed in the small intestine and is stored in the liver. It works by assisting in the production of myelin, a protective sheath around nerves, and helps in the formation of red blood cells. Additionally, it supports cellular energy production by converting carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into energy.
2. Benefits of Vitamin B12
2.1. Energy Boost and Fatigue Reduction
One of the most noticeable benefits of Vitamin B12 is its role in energy metabolism. It helps in converting food into glucose, which the body uses for energy. A deficiency in Vitamin B12 can lead to fatigue, weakness, and decreased energy levels. By maintaining adequate levels of Vitamin B12, you can support your energy levels and combat fatigue.
2.2. Supports Nervous System Health
Vitamin B12 is essential for the health of the nervous system. It helps in maintaining the integrity of the myelin sheath, which insulates nerve cells and ensures proper nerve function. Adequate levels of Vitamin B12 can prevent neurological problems such as numbness, tingling in the hands and feet, and cognitive difficulties.
2.3. Enhances Red Blood Cell Production
Vitamin B12 plays a crucial role in the production of red blood cells. It helps in the formation of healthy red blood cells by aiding in the synthesis of DNA and RNA. A deficiency in Vitamin B12 can lead to anemia, characterized by a reduced number of red blood cells, leading to symptoms such as paleness, dizziness, and shortness of breath.
2.4. Supports Cognitive Function
Maintaining adequate levels of Vitamin B12 is linked to better cognitive function. It is involved in the synthesis of neurotransmitters, which are essential for communication between nerve cells. Low levels of Vitamin B12 have been associated with cognitive decline and increased risk of neurodegenerative conditions.
2.5. Improves Mood and Mental Health
Vitamin B12 plays a role in the synthesis of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that regulates mood. Deficiency in Vitamin B12 has been linked to symptoms of depression and mood disturbances. By ensuring sufficient levels of Vitamin B12, you can support mental health and overall emotional well-being.
3. Sources of Vitamin B12
3.1. Dietary Sources
Vitamin B12 is naturally found in animal-based foods. Key sources include:
- Meat: Beef, pork, and lamb are excellent sources of Vitamin B12.
- Poultry: Chicken and turkey provide good amounts of Vitamin B12.
- Fish: Salmon, trout, and sardines are rich in Vitamin B12.
- Dairy Products: Milk, cheese, and yogurt contain Vitamin B12.
- Eggs: Eggs, particularly the yolks, are a source of Vitamin B12.
3.2. Fortified Foods
For those following a vegetarian or vegan diet, obtaining Vitamin B12 from fortified foods is crucial. Many plant-based milk alternatives, breakfast cereals, and nutritional yeast are fortified with Vitamin B12 to help meet dietary needs.
3.3. Supplements
Vitamin B12 supplements are available in various forms, including tablets, capsules, and sublingual (under-the-tongue) preparations. For individuals who have difficulty absorbing Vitamin B12 from food sources, supplements can be an effective way to ensure adequate intake.
4. Signs and Symptoms of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
4.1. Fatigue and Weakness
One of the most common symptoms of Vitamin B12 deficiency is fatigue and weakness. Since Vitamin B12 is essential for red blood cell production, a deficiency can lead to anemia, resulting in decreased oxygen delivery to tissues and a feeling of tiredness.
4.2. Numbness and Tingling
Deficiency in Vitamin B12 can cause neurological symptoms, such as numbness and tingling in the hands and feet. This is due to the role of Vitamin B12 in maintaining the myelin sheath that protects nerve cells.
4.3. Cognitive Difficulties
Vitamin B12 deficiency can lead to cognitive difficulties, including memory loss, confusion, and difficulty concentrating. Severe deficiencies may result in more serious neurological conditions, such as dementia.
4.4. Pale Skin and Shortness of Breath
Anemia caused by Vitamin B12 deficiency can lead to pale skin and shortness of breath. The lack of healthy red blood cells impairs oxygen transport, causing these symptoms.
4.5. Mood Changes
Mood disturbances, including depression and irritability, can be linked to Vitamin B12 deficiency. The vitamin’s role in neurotransmitter synthesis affects mood regulation.
5. How to Maintain Optimal Vitamin B12 Levels
5.1. Regular Dietary Intake
Consuming a balanced diet that includes Vitamin B12-rich foods is essential for maintaining optimal levels. For individuals who follow a vegetarian or vegan diet, it is important to include fortified foods or consider supplements to meet Vitamin B12 needs.
5.2. Regular Check-Ups
Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help monitor Vitamin B12 levels, especially for individuals at higher risk of deficiency, such as the elderly, vegetarians, and those with gastrointestinal conditions.
5.3. Supplements
For individuals who have difficulty absorbing Vitamin B12 or who are at risk of deficiency, supplements can be a valuable addition to the diet. Consult with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dosage and form of Vitamin B12 supplement.
5.4. Addressing Absorption Issues
Certain medical conditions and medications can affect Vitamin B12 absorption. For individuals with absorption issues, such as those with pernicious anemia or gastrointestinal disorders, specialized treatments or higher doses of Vitamin B12 may be necessary.
6. The Science Behind Vitamin B12
6.1. Research and Studies
Extensive research has demonstrated the vital role of Vitamin B12 in various aspects of health. Studies have confirmed its importance in red blood cell formation, neurological function, and cognitive health. Research continues to explore the full extent of Vitamin B12’s impact on health and its potential therapeutic uses.
Key Studies:
- Vitamin B12 and Anemia: Research has established the link between Vitamin B12 deficiency and anemia, highlighting the vitamin’s role in red blood cell production.
- Cognitive Function: Studies have shown that adequate Vitamin B12 levels are associated with better cognitive function and a reduced risk of cognitive decline.
- Mood Regulation: Research indicates that Vitamin B12 deficiency can contribute to mood disturbances and that supplementation may improve mood and mental health.
6.2. Mechanisms of Action
Vitamin B12 acts as a cofactor in various biochemical reactions, including the synthesis of DNA, RNA, and neurotransmitters. It is essential for the metabolism of fatty acids and amino acids, contributing to overall energy production and cellular function.
Importance of Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is crucial for several bodily functions, including:
1. Energy Production: It helps convert food into energy, reducing fatigue.
2. Nerve Health: Supports the maintenance of the nervous system, preventing nerve damage.
3. Red Blood Cell Formation: Essential for the production of healthy red blood cells, preventing anemia.
Benefits of WellHealthOrganic Vitamin B12
 WellHealthOrganic Vitamin B12 supplements offer several benefits:
WellHealthOrganic Vitamin B12 supplements offer several benefits:
– Improved Energy Levels: Regular intake can combat tiredness and boost energy.
– Enhanced Brain Function: It may improve memory and reduce the risk of cognitive decline.
– Better Mood Regulation: B12 supports serotonin production, which can enhance mood and reduce symptoms of depression.
Who Needs Vitamin B12?
Certain groups are more at risk of B12 deficiency:
– Vegans and Vegetarians: B12 is mainly found in animal products, making supplements crucial for those on plant-based diets.
– Older Adults: Absorption decreases with age, increasing the risk of deficiency.
– Individuals with Digestive Disorders: Conditions like Crohn’s disease or celiac disease can hinder absorption.
Signs of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
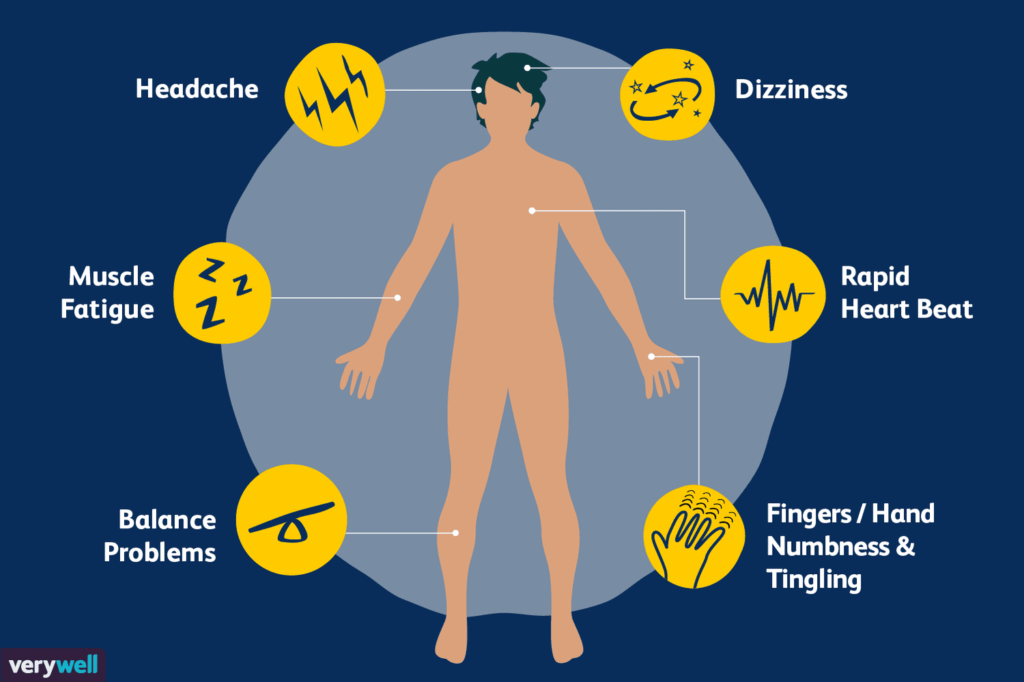
Common symptoms of deficiency include:
– Fatigue and weakness
– Pale or jaundiced skin
– Nerve problems, like tingling or numbness
– Difficulty thinking and memory loss
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Product Name | Wellhealthorganic Vitamin B12 |
| Form | Tablets, Capsules, Sublingual Drops |
| Active Ingredient | Methylcobalamin |
| Dosage | 1000 mcg per tablet/capsule/drop |
| Recommended Use | 1 tablet/capsule/drop daily or as directed by a healthcare provider |
| Bioavailability | High, due to the use of Methylcobalamin |
| Suitable For | Vegetarians, Vegans, Older Adults, Athletes |
| Free From | Gluten, Soy, Dairy, Artificial Colors, and Preservatives |
| Certifications | GMP Certified, Third-Party Tested |
| Packaging | Recyclable, BPA-Free Containers |
| Storage Instructions | Store in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight |
| Shelf Life | 2 years from the date of manufacture |
| Health Benefits | Energy Boost, Improved Mental Clarity, Red Blood Cell Formation, Neurological Health |
| Potential Side Effects | Rare; may include dizziness, headache, nausea |
| Price Range | $15 – $30 per bottle (60 tablets/capsules/drops) |
| Availability | Online and in select health stores |
| Customer Rating | 4.8/5 based on customer reviews |
| Company Mission | Promote holistic health through high-quality, natural supplements |
| Customer Support | 24/7 support via email and phone |
What is Vitamin B12?

Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin that plays a pivotal role in the functioning of the brain and nervous system. It’s also essential for the formation of red blood cells and DNA synthesis. Chemically, it contains the mineral cobalt and can be found in several forms, including cyanocobalamin and methylcobalamin.
Benefits of Vitamin B12

Energy Production
One of the primary benefits of Vitamin B12 is its role in energy production. It helps convert carbohydrates into glucose, which your body uses for energy. If you’re feeling fatigued, low B12 levels might be the culprit.
Red Blood Cell Formation
Vitamin B12 is essential for the production of red blood cells. Without adequate B12, red blood cells can become abnormally large and fail to divide properly, leading to anemia.
Neurological Health
Vitamin B12 plays a significant role in maintaining neurological health. It helps in the production of myelin, a protective sheath that covers your nerves. A deficiency can lead to neurological issues, including memory loss and mood changes.
DNA Synthesis
Every cell in your body needs DNA to function properly. Vitamin B12 is crucial for DNA synthesis, ensuring that cells divide correctly and function optimally.
Conclusion
Vitamin B12 is a critical nutrient with far-reaching effects on health, from energy production and red blood cell formation to cognitive function and mood regulation. Ensuring adequate intake through diet, fortified foods, or supplements is essential for maintaining optimal health and preventing deficiency-related issues.